Become a Knowledge Stack (RAG) Expert
OG Msty users loved Knowledge Stacks, where RAG is done right.
With Msty Studio, we’ve made it even simpler and more powerful to create, manage, and leverage Knowledge Stacks for your AI applications.
To help you get the most out of them, we’ve put together a Knowledge Stacks YouTube series, an 11-episode guide that takes you from the basics to expert-level best practices.
Here’s a quick look at what’s inside.
Episode 1: Knowledge Stacks Introduction
Want to get started quickly? This video provides a quick run-through of how to create a Knowledge Stack in Msty Studio using all of the default settings.
This is perfect for those who want to get up and running quickly without diving into the more advanced settings.
Episode 2: Adding Files and Folders to a Knowledge Stack
One of the most important steps in creating a Knowledge Stack is to gather clean, relevant data.
Using Knowledge Stacks, or any RAG system, is only as useful as the data you provide it. It is important that you assess the quality of the data, ensuring it is current, relevant, and accurate. If you feed in bad data, you'll get bad results.
This video walks through adding files and folders to the Knowledge Stack as well as different load modes that are available for file uploads.
By default, files are cached when you first upload them and Msty Studio will use the cached files when re-composing Knowledge Stacks.
However, if you have files that are frequently updated, you can choose one of the following load methods:
- Dynamic Mode - this will pull the latest version of the file when re-composing the Knowledge Stack
- Sync Mode - with this selected, Msty Studio will monitor the file for changes then automatically re-compose the Knowledge Stack when a change is detected
Episode 3: Ignore Settings for Folder Uploads
When uploading folders, you may want to exclude certain files or file types from being added to the Knowledge Stack.
This can be done by adding a mstyignore file to the root of the folder you are uploading.
You can also select the ellipsis icon next to the Knowledge Stack folder name on the left side of the screen to set ignore rules for all Knowledge Stacks within that folder.
Ignore rules are for folder uploads only and will not apply to individual file uploads.
Episode 4: Enable File Sync Mode
In this video, we dive more into the Sync Mode option for file uploads, how you can enable Msty Studio to monitor files for changes, and we show a quick example.
Episode 5: Compose Settings
Compose Settings allow you to configure which Embedding Model will be used, which we'll cover more in depth in Episode 6, as well as setting chunking method (recursive versus sentence), chunk size, chunk overlap, and chunk sizes to ignore.
Before your data is "vectorized", it is first broken down into smaller pieces, or "chunks". This is important because most AI models have a limit to how much text they can process at one time.
The Embedding Model is not important in the chunking process and Msty Studio will chunk the data the same way, according to the configs you set, regardless of which Embedding Model you choose.
Additionally, you want to consider the conversation model you plan to use with the Knowledge Stack. For example, if you plan to use a model with a smaller context window, you may want to use smaller chunks to ensure that more relevant information can fit within the model's context window during a conversation.
Overall, you are looking for a goldilocks chunk size that is not too big and not too small. Ideally, the chunk will be just the right size to provide enough context for the AI model to generate accurate and relevant responses without overwhelming it with too much information at once.
If using the recursive chunking method, the amount of character overlap between chunks is also important. You want to ensure that there is enough overlap to maintain context between chunks, but not so much that it creates redundancy and increases the overall size of the Knowledge Stack unnecessarily. As well as not too little where the overlapping text is not enough to maintain context between chunks.
Episode 6: Evaluating Embedding Models
Choosing the right Embedding Model is crucial for the performance of your Knowledge Stack.
Embedding Models are responsible for converting your text data into numerical vectors that can be easily processed by AI models. Different Embedding Models have different strengths and weaknesses, so it's important to choose one that is well-suited to your specific use case.
Online vs Local Embedding Models
One key decision is to decide between using an online or local Embedding Model. Here are some considerations for each:
| Online | Local |
|---|---|
| Data is sent to provider | Run locally on your device |
| Some providers offer options to opt out of data retention and/or model training | More secure method if you have sensitive data and don’t want to share with online providers |
| Some providers offer enterprise or private instances, which typically offer more security if you choose to use an online provider | No additional cost - performance largely dependent on your hardware running the model |
| Be sure to check their security policies and agreements | May not be as ‘performant’ as online provider models; but most will get the job done the same for what you’ll need |
| Factor in cost considerations | |
| Performance is typically good but dependent on internet connection, provider’s infrastructure, etc |
Top Online & Local Embedding Models
Wondering which specific Embedding Models to use? Here are some current popular options which, as with anything AI, is sure to change any moment. 😅
| Online | Local |
|---|---|
| Cohere Embed v3 (1024) | Arctic Embed 335M (1024) |
| Gemini Embedding 004 (768) | MixedBread Embed Large (1024) |
| OpenAI Embedding 3 Large (3072) | Stella-en-1.5B-v5 (1024) |
| Voyage-3-large (1024) | Nomic Embed Text v1.5 (768) |
| Jina Embeddings v3 (1024) | Gte-tiny Msty Default (384) |
| NV Embed v2 (4096) |
What to look for
Need some additional guidance on choosing the right Embedding Model? Here are some key factors to consider:
- Evaluate your own data
- Don’t rely solely on “benchmarks”
- Test search results - what is actually going to be provided to model as context
- Knowledge domains
- Use what’s best for coding, research, medical, a language, etc
- How many files are you converting?
- Small amount of docs? Look for quality and larger models
- Large amount of docs? Look for efficiency and smaller models
- Dimensions
- Dimensions represent the size of the vector that each piece of text, or chunk, gets converted into that captures the semantic meaning
- Sweet spot is considered to be around 768-1024 dimensions
- Diminishing returns beyond 1024-1536 for most use cases
- Smaller dimensions = faster similarity calculations
In this video, we also walkthrough the process of embedding text data into vector representations and dimensions. Below is the image used to illustrate this process - right click to open in new window for a large view.
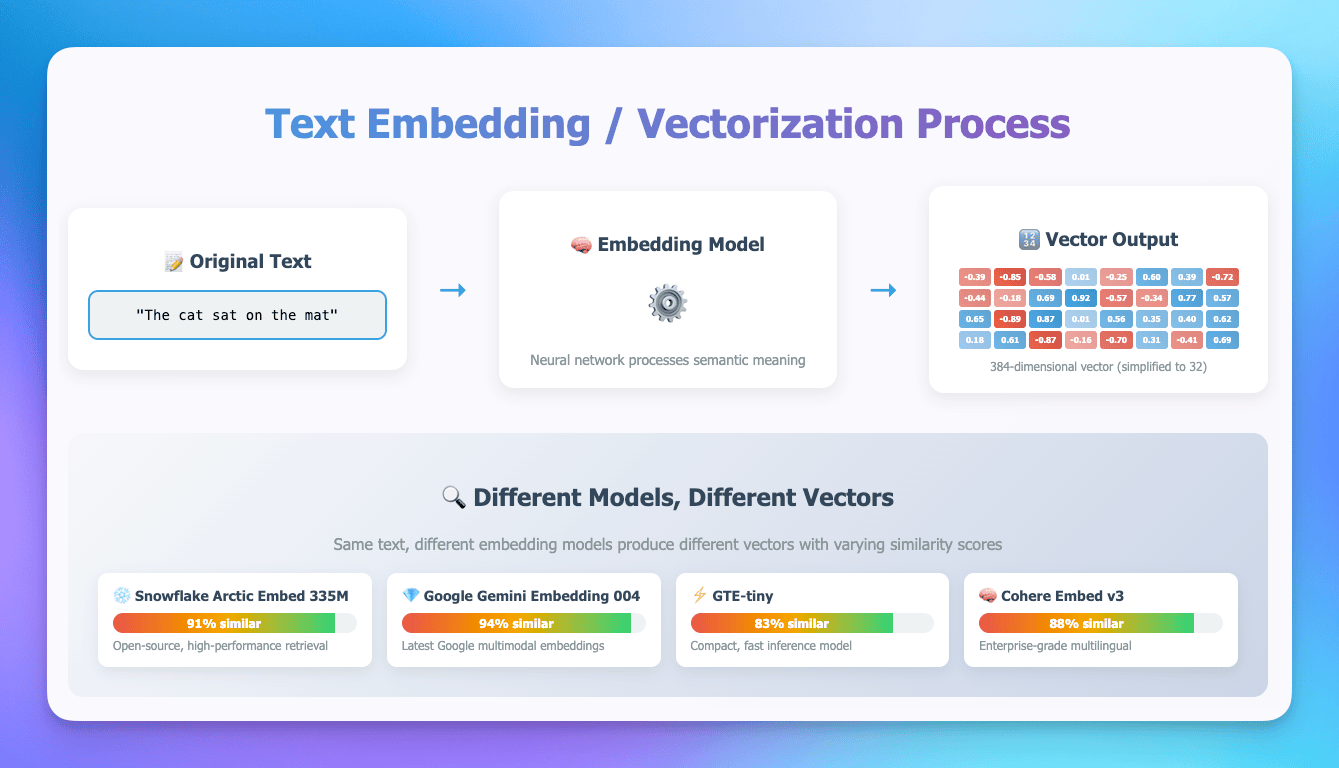
Episode 7: Query Settings
This is another critical step to avoid overwhelming the model with unnecessary information. Once again, the goal is to find the goldilocks zone - not too much context, but just enough to get the best results.
Episode 8: Scrub Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
Chances are, if you are using your own data, it may contain some form of Personally Identifiable Information (PII). Or, PII of others.
If you intend to enable a Knowledge Stack with an online model during a conversation, we recommend to enable PII scrubbing to avoid sending senstive PII information to the online Provider.
When enabling PII Scrubber, select a local model to run through your data locally and anonymize the data with generic placeholders.
This way, you can leverage the power of online models while keeping sensitive information private and secure.
Episode 9: Full Content Context
One of the most frequent questions we heard with Knowledge Stacks in Msty v1.x was "Why do summaries sometimes feel incomplete or off?"
This is a common challenge with RAG systems in general.
Here’s why: when you ask a question, RAG retrieves small chunks of text from your documents that best match your query. But those chunks rarely represent the entire document. And when it comes to summarizing, you need the full context to do it well.
With Msty Studio, we’ve introduced Full Content Context, a feature that automatically includes the full document when it’s necessary, like when you ask for a detailed summary.
Just another way Msty makes RAG work the way you expect. 😉
Episode 10: Optimize for Local Models
If you're using Knowledge Stacks with local models, you may notice that some local models don't seem to answer questions all that well out of the box.
This is typically due to the smaller context windows that local models have compared to their cloud-based counterparts.
But don't fret! This video covers some tips and tricks to help you get the most out of local models, such as:
- Ensuring chunk sizes are right-sized
- Adjusting query settings to avoid overwhelming the model with too much context
- Increasing the context window for the local model
Episode 11: Reports and More!
In this last video, we explore the Reports and Analytics feature where you can see how your Knowledge Stacks are performing and how you can optimized them.
We also showcase other features that we didn't cover in previous episodes.
Final Thoughts
Knowledge Stacks have come a long way since Msty v1.x, and with Msty Studio, they’re more powerful, flexible, and easier to manage than ever.
Whether you’re just getting started or fine-tuning advanced RAG systems, this series gives you the tools and best practices to get the most from your data.
Want to go deeper? Explore the full Knowledge Stacks Documentation here to master every feature, and start building smarter, faster, and more reliable AI-powered workflows with Msty Studio.
Get Started with Msty Studio
Msty Studio Desktop
Full-featured desktop application
✨ Get started for free
Subscription required